|
Products
Database Search Solution (New Version) Search Control SEO Pager Highlighter Shortcut Controls Crypt Package Free ASP.NET Controls
Geotargeting Component ASP.NET Media Player Control Flash Video Player Control Services
ASP.NET Telecommute Jobs Free IP Location Lookup Test .Net Regular Expressions CSS/Table/DIV Page Layouts Custom Programming Article Sites Master List |
Caching in an ASP.NET 2.0 Web ApplicationCaching OverviewCaching is the most effective technique you can use to improve the performance of your ASP.NET web application. Designing your application with caching in mind, improves both the performance and the scalability of that application. Caching is about storing data in memory the first time it is requested and then re-using it for the following requests for a specified period of time. ASP.NET provides you with two types of caching that you can use to create a high performance web application. The first type is application caching in which you can store application's data in server memory for subsequent requests without recreating them each time. This saves the time and the resources of your application. The second type is output caching. In this type you can save or let us say you can cache dynamic pages and / or user controls for subsequent requests without the need to execute them everytime. In this tutorial we will explore those caching techniques, in addition to some new features available only in ASP.NET 2.0 To download the complete example we will discuss in this tutorial, please click here. Type 1: Caching Application DataASP.NET provides an easy to use caching mechanism. Simply, you can store data that require extensive server resources to be created. By caching this data you are creating it once and then using it many time without recreating that data again. This can improve your application performance significantly. You can cache your application data by using the cache class. The instance of this class is private to each application. The life time of this class is the life time of the application itself. The cache object is recreated each time the application is restarted. The cache object is global, means the data stored in it is available anywhere within the web application, and in this regard this is similar to the application object. The difference between the cache object and the application object is that the cache object has some more powerful features that allows you to control the cached data. With the cache object, each item or data stored in the cache object can have its priority state, and can have an expiration time. The Cache object uses those two features in situation like this: When your system's memory becomes scarce, the cache object chooses items with low priority or seldom use to remove and this frees memory. This is how the cache object ensures that unnecessary items does not consume valuable server resources. Storing Data in the Cache object You can store data in the cache object using several approaches: using simple assignment, using the 'Add' method, and using the 'Insert' method. Here's some lines of code that demonstrate the 3 approaches:
You can store data in the cache object in the form of key-value pairs as shown in the previous example. By using the 'Add' method you can set more parameters other than the key / value. You can set the expiration time, the priority, the dependency on another object, and a notification to your application to be sent when that key is deleted from the cache. Using the 'Insert" method you can simply create a new key and assign a value to it. You can still optionally set other parameters like in the 'Add' method. Retrieving Data from the Cache object You can access the cached data by using their keys just like the 'Session' and 'Application' objects, but before attempting to retrieve a cached value you must check for its existence as shown in the following example:
If you run this code you will get the following: 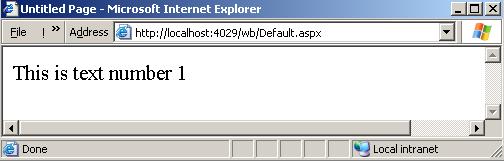 Figure 1 Removing Data from the Cache Object To remove a given key from the cache object, just use the 'Remove' method and supply the name of the key you need to remove as in the following line of code.
If you now run the application after removing this key, you will get the following: 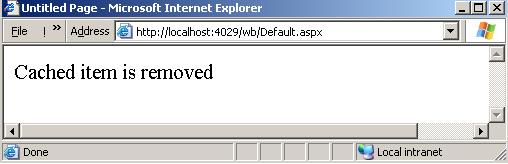 Figure 2 Responding to Removed Cached Data When you use the 'Add' method or the 'Insert' method to add new data to your cache object, you can specify an 'OnRemove' callback function that will be called when the data is removed. This is the only event the cache object can provide. To see how this could be done let's see the following example with the code associated with the callback is shown in boldface for more clarity.
In the above code we declare an OnRemove callback function for the 'Key2' cached item and associate it with the 'Key2Removed' subroutine which stores the removed item key and value plus the reason of removal in an application state key called 'Status'. Then, we add a button control named 'Button_Key2' and activate its 'OnClick' event handler. In this handler we display the value stored in the 'Key2' cached item, then we display a text box that says that this item will be removed from the cache object now. After the user click on the 'Ok' button of this text box the application state item 'Status' will be displayed indicating that the 'Key2' cached item is already removed from the cached object. You can display and review the complete code if you download the complete example from this link. Type2: Caching ASP.NET PagesASP.NET allows you to cache web pages or portions of them, calling this an output caching. By caching frequently requested pages or portions of them, you can substantially increases your web server throughput and get a fast page response. You can cache pages on devices like: the web browser making the request, the web server responding to the request, and any other cache capable devices such as proxy servers. There are two ways you can use for output caching: declaratively in a page / a configuration file, or programmatically using a cache API. Using the OutputCache Directive You can use the @OutputCache directive to cache your web page or form in a declarative way. The OutputCache directive has the following attributes: Duration: Specifies how long the page
will be cached, measured in
seconds. Let's now see some real code of how to cache an entire web page or web form ... In the web form .aspx source view, add the following code:
The above code caches only one response of the entire web page or form for a duration of 60 seconds on the server. When the web form is requested for the first time, the server creates it and stores it for subsequent requests. After 60 seconds the cached page will expire. If the page is requested after that expiration time, the server will recreate it again and store it for another 60 seconds, and so on. You can use OutputCache's other attributes to cache multiple responses of a single web form using the VaryByParam attribute. You can cache portions of web forms using the VaryByControl attribute. Caching with code The above technique shows you how to cache a web form using the OutputCache directive in a declarative way, now we will explain how you can do the same task using code. The following code demonstrate how to use caching programmatically.
The above code is, simply, equivalent to the following line:
For further informationRefer to the online copy of Microsoft Developers Network at http://msdn.microsoft.com or use your own local copy of MSDN. Tutorial toolbar: Tell A Friend | Add to favorites | Feedback | |

