|
Products
Database Search Solution (New Version) Search Control SEO Pager Highlighter Shortcut Controls Crypt Package Free ASP.NET Controls
Geotargeting Component ASP.NET Media Player Control Flash Video Player Control Services
ASP.NET Telecommute Jobs Free IP Location Lookup Test .Net Regular Expressions CSS/Table/DIV Page Layouts Custom Programming Article Sites Master List |
Working with Web User Controls at Run-timeIntroductionIn addition to HTML and Web server controls, ASP.Net provides with the capability to easily create custom reusable controls by using the same techniques that are used to develop an ASP.Net page. These controls are called user controls. User controls offer great flexibility than server-side includes (SSIs) by accessing the object model support provided by ASP.NET. Using User Controls you can program against any properties declared in the control just like any other ASP.Net server control, rather than simply including the functionality provided by another file. Furthermore, in a single application, multiple user controls can exist that are authored using different languages. For example, an application can have a user control created with Visual Basic while another in C#, and have both these controls on the same ASP.Net page. In this article I will create a simple login user control, and load that to a web-page dynamically.
PrerequisitesThis tutorial assumes that you own a copy of Visual Studio 2005 or Visual Web Developer Express. It also assumes that you are familiar with ASP.Net 2.0 basics and have worked with user controls before.
Creating the WebsiteIf you have an existing web site, you can skip this section. Otherwise, you can create a new web site and page by following these steps. To create a file system Web site:
The New Web Site dialog box appears.
For example, type the folder name C:\WebSites\mySite.
Visual Web Developer creates the folder and a new page named Default.aspx
Adding a User Control to the WebsiteRight-click in the solution explorer and select Add New Item. Select Web User Control and type in the name of the control. Click on Add to add the user control to the web application.
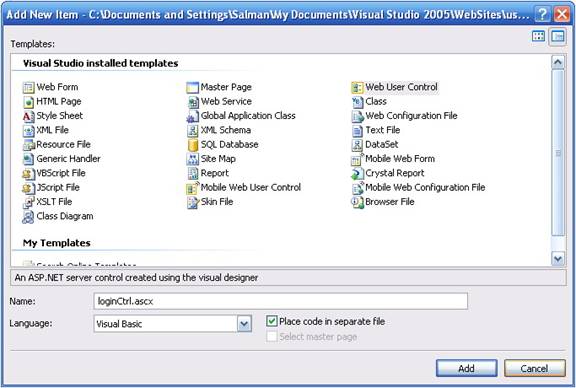
This will add a .ASCX file to the project. This is our user control.
Preparing our ControlDouble click loginCtrl.ascx to open the new user control and switch to design view. Add a table to the page by clicking Inset Table under the Layout Menu. Design a page similar to the following:
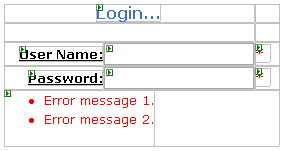
As you can see, this user control defines a typical Login Control. I also added two Required Field Validation controls and a Validation Summary control. Make sure that the ControlToValidate properties of the validation controls are set, otherwise the application will result in an error at run-time. Now, switch to the code-behind of the user control. I am going to add property methods to retrieve the values entered in the text-boxes.
Partial Class loginCtrl Inherits System.Web.UI.UserControl
Property pUser() As String Get Return txtUser.Text.Trim End Get Set(ByVal value As String) txtUser.Text = value End Set End Property
Property pPass() As String Get Return txtPassword.Text End Get Set(ByVal value As String) txtPassword.Text = value End Set End Property End Class
This completes our user-control. You can create a much advanced user-control by adding login button to the user-control and handling the login functionality in the control itself. This way you can completely separate the login functionality from the presentation layer.
Adding the control to the Web-Page at design timeFirst we will try out our control by adding it to the Default.aspx page at desing-time. Open Default.aspx and switch to Design-view. Now click on loginCtrl.ascx in the solution explorer and drag it onto Default.aspx. This will add the user control onto the page, just like it does a server control.
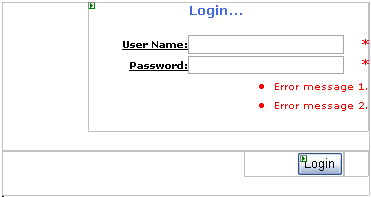
After adding the control, I created a login button on the page. Switch to code-behind class and create a button event handler for the login button.
Protected Sub btnLogin_Click(_, _) Handles btnLogin.Click Dim tempString As String = "" tempString = "UserName: " + Me.LoginCtrl1.pUser tempString = tempString + "... " tempString = tempString + "Password: " tempString = tempString + Me.LoginCtrl1.pPass + "." Response.Write(tempString) End Sub
This will fetch the user-name and password from the user control and write it onto the web-page.
Compile and run the web-application. Using planned layout, you can create professional and eye-catching applications with ASP.Net easily. With the use of User Controls, you can keep your presentation layer from your data and business layer.
Adding the control to the Web-Page at run-timeThe main focus of this article was in explaining how to setup a user control to be loaded on a page at run-time. This is a very important and useful technique in creating ASP.Net applications. For instance, you have created two menus, one is an administrator menu, and the other is the basic user menu_ Based on the login credentials you can easily identify the user of your site as a simple client or an administrator. Thus, you can load whichever user control as required at run-time.
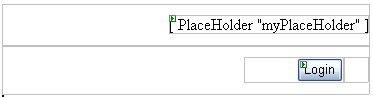
In the Default.aspx page, switch to design-view and delete the loginCtrl.ascx that we earlier dragged onto the page. Go to ToolBox and drag-n-drop a PlaceHolder where the User Control had been. This place holder will hold our user control, i.e. at run-time, I will add the user control to this placeholder. Switch to the code-behind class and make changes to the code in order to have the following:
Protected Sub Page_Load(_, _) Handles Me.Load Dim tempControl As Control = LoadControl("loginCtrl.ascx") Me.myPlaceHolder.Controls.Add(tempControl) End Sub
Protected Sub btnLogin_Click(_, _) Handles btnLogin.Click Try For Each tempControl As loginCtrl In myPlaceHolder.Controls Dim tempString As String = "" tempString = "UserName: " + tempControl.pUser tempString = tempString + "... " tempString = tempString + "Password: " tempString = tempString + tempControl.pPass + "." Response.Write(tempString) Next Catch ex As Exception
End Try End Sub
The loadControl function is used to create an instance of the user control at run-time. You can define a static path to the .ascx file or a dynamic path. Using the dynamic approach can create the application more portable. Next follows the changes to the Button handler. What we do in this event handler is locate the loginCtrl instance inside the place holder. If it was successfully loaded, then it would exist. The rest is the same as before. Taking into consideration our two-menu example, in the button event-handler, we will loop for both controls. On page load, one of the menu is added, and thus the code for that will be executed, while since the other won't exist.
And all things must come to an endThe main emphasis in this article was on ASP.Net 2.0 User Control - A dynamic approach. Though simple, this approach is unknown to a vast range of developers. Using User Controls in one's ASP.Net application makes the web-site more robust and adaptable. I hope you found this article interesting and informative. I am open for suggestions and remarks, both negative and positive. Feel free to contact me at salman@premierpos.com. Tutorial toolbar: Tell A Friend | Add to favorites | Feedback | |

